3.5 标牌点和融入点
Signage Points and Infusion Points
挑战链和奖励链中的每个子时隙都分为 64 个较小的 VDF。在这些较小的 VDF 之间有一个点,称为 标牌点。时间领主在到达每个标牌点时发布 VDF 输出和证明。
挑战链和奖励链都有标识点。然而,注入的挑战链却没有。
标牌点每 9.375 秒出现一次(每 600 秒子时隙 64 个标牌点)。每个标牌点之间的迭代次数为标牌点间隔迭代次数,等于子时隙迭代次数 / 64。
子时隙开始处的挑战也是一个有效的标牌点。当到达子时隙中的 64 个标牌点中的每一个时,这些点将被广播,从最快的时间领主的完整节点开始,并传播到网络上的所有其他完整节点。
农民收到这些标牌点并在每个标牌点计算每个地块的哈希值。如果哈希以九个零开头,则绘图通过该标牌点的过滤器,并且可以继续。对于该标牌点,这将取消网络中所有绘图文件的大约 511/512 的资格。计算过滤器哈希的公式是:
plot filter bits = sha256(plot id + sub slot challenge + cc signage point)
空间挑战的证明计算为绘图过滤器位的散列:
pos challenge = sha256(plot filter bits)
使用这个挑战,农民为每个通过过滤器的地块获取高质量的字符串。 回想一下,这个过程需要大约 7 次随机磁盘寻道,这在慢速 HDD 上需要大约 70 毫秒。 质量字符串是从空间证明的一部分派生的哈希(但尚未检索整个空间证明)。
对于我们的 上一个示例以及下一个示例,我们将使用以下值:
- 子时隙迭代次数 = 100,000,000
- 标牌点间隔迭代次数 =
子时隙迭代次数/ 64 = 1,562,500
原文参考
Each sub-slot in both the challenge chain and the reward chain is divided into 64 smaller VDFs. Between each of these smaller VDFs is a point called a signage point. Timelords publish the VDF output and proof when they reach each signage point.
The challenge and reward chains both have signage points. The infused challenge chain, however, does not.
The signage points occur every 9.375 seconds (64 signage points per 600-second sub-slot). The number of iterations between each signage point is sp_interval_iterations, which is equal to sub-slot_iterations / 64.
The challenge at the start of the sub-slot is also a valid signage point. As each of the 64 signage points in the sub-slot is reached, those points are broadcast, starting from the fastest timelord's full node, and propagating to every other full node on the network.
Farmers receive these signage points and compute a hash for each plot, at each signage point. If the hash starts with nine zeros, the plot passes the filter for that signage point, and can proceed. This disqualifies around 511/512 of all plot files in the network, for that signage point. The formula to compute the filter hash is:
plot filter bits = sha256(plot id + sub slot challenge + cc signage point)
The proof of space challenge is computed as the hash of the plot filter bits:
PoSpace challenge = sha256(plot filter bits)
Using this challenge, the farmers fetch quality strings for each plot that made it past the filter. Recall that this process requires around seven random disk seeks, which takes around 70 ms on a slow HDD. The quality string is a hash derived from part of the proof of space (but the whole proof of space has yet to be retrieved).
For both of our previous example, as well as the next example, we'll use the following values:
- sub-slot_iterations = 100,000,000
- sp_interval_iterations =
sub-slot_iterations/ 64 = 1,562,500
农民为每个空间证明计算 所需迭代次数。如果所需迭代次数 < 标牌点间隔迭代次数,则空间证明有资格包含在区块链中。 此时,农民从磁盘中获取整个空间证明(这需要 64 次磁盘寻道,或在慢速 HDD 上需要 640 毫秒),创建一个未完成的块,并将其广播到网络。
对于绝大多数符合条件的地块,所需迭代次数会太高,因为平均每个 10 分钟子时隙有 32 个符合整个网络的条件。这是一个随机过程,因此有可能(尽管不太可能)大量证明符合条件。标牌点迭代次数是从子时隙开始到标牌点的迭代次数。 任何满足标牌点所需迭代次数的地块都将符合资格,因为获胜地块之间没有竞争。
required_iterations 的确切方法如下:
sp_quality_string = sha256(quality_string + cc_signage_point)required_iterations = (difficulty * difficulty_constant_factor * int.from_bytes(sp_quality_string, "big", signed=False) // pow(2, 256) * expected_plot_size(size))难度常数因子基于区块链的初始常数。对于奇亚,它是 2^67。难度因时期而异,如第 3.11 节中所述。 如您所见,标牌点质量字符串 被转换为 0 到 1 之间的随机数,通过将其除以 2^256,然后乘以绘图大小。
出于共识的目的,预期图块大小 是 ((2 * k) + 1) * (2 ** (k - 1)).,其中 k >= 32 < 50。 实际绘图大小是该值乘以一个常数因子,以字节为单位。这是因为图中的每个条目大约是k+0.5位,并且大约有2^(k)个条目。
融合迭代次数 是从子时隙开始的迭代次数,在此迭代次数至少具有所需质量的块可以被包含到区块链中。这计算如下:
融合迭代次数 =( 标牌点迭代次数 + 3 * 标牌点间隔迭代次数 + 所需迭代次数) % 子时隙迭代次数
原文参考
The farmer computes the required_iterations for each proof of space. If the required_iterations < sp_interval_iterations, the proof of space is eligible for inclusion into the blockchain. At this point, the farmer fetches the entire proof of space from disk (which requires 64 disk seeks, or 640 ms on a slow HDD), creates an unfinished block, and broadcasts it to the network.
For the vast majority of eligible plots, required_iterations will be far too high, since on average 32 will qualify for the whole network for each 10-minute sub-slot. This is a random process so it's possible (though unlikely) for a large number of proofs to qualify. The signage_point_iterations is the number of iterations from the start of the sub-slot to the signage point. Any plot that does meet the required_iterations for a signage point will qualify as there is no rivalry between winning plots.
The exact method for required_iterations is the following:
sp_quality_string = sha256(quality_string + cc_signage_point)required_iterations = (difficulty * difficulty_constant_factor * int.from_bytes(sp_quality_string, "big", signed=False) // pow(2, 256) * expected_plot_size(size))The difficulty constant factor is based on the initial constants of the blockchain. For Chia, it is 2^67. The difficulty varies per epoch, as explained in Section 3.11. As you can see, the sp_quality_string is converted into a random number between 0 and 1, by dividing it by 2^256, and then multiplied by the plot size.
For consensus purposes, the expected_plot_size is ((2 * k) + 1) * (2 ** (k - 1))., where k>=32<50. The actual plot size is that value times a constant factor, in bytes. This is because each entry in the plot is around k+0.5 bits, and there are around 2^(k) entries.
The infusion_iterations is the number of iterations from the start of the sub-slot at which the block with at least the required quality can be included into the blockchain. This is calculated as:
infusion_iterations = ( signage_point_iterations + 3 * sp_interval_iterations + required_iterations) % sub-slot_iterations
因此,infusion_iterations 将在当前标牌点之后的 3 到 4 个标牌点之间。农民必须在到达融入点之前提交他们的证明和块。如果标牌点靠近子时隙的末端,则模数允许溢出到下一个子时隙中。这在第 3.9 节中进行了扩展。
有关融入点的更多信息,请参见第 3.3 节。
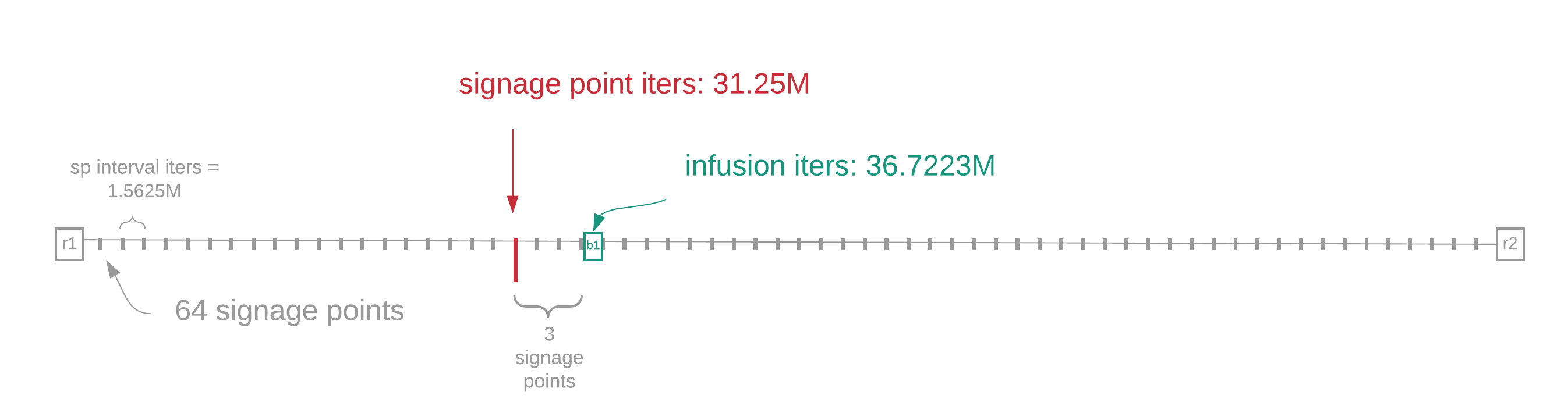
图 5 将融入点显示为标有“b1”的绿色方块。子时隙的第一个和最后一个块分别标记为“r1”和“r2”。在这个例子中,农民将在标有红色箭头的标牌点处创建块,我们将其称为“b1”。
在“b1”处,农民的块与该点的 VDF 输出组合在一起。从那时起,这将为 VDF 创建一个新的输入,即我们将农民的块注入 VDF。 b1 仅在两个事件发生后才完全有效:
- 已达到融合迭代次数,并且
- 包含两个 VDF 样张:一个从
r1到标牌点,一个从r1到b1。 (实际上更多,因为有三个 VDF 链,在第 3.8 节中有解释)。
在图 5 中,农民在标志点“b1”处创建了块。但是,“b1”还没有完成,因为它需要注入点 VDF。一旦融合迭代 VDF 被释放,它就会被添加到“b1”以在“b1”处形成完成的块。
回想一下,在这个例子中,
- 子时隙迭代次数 = 100M
- 标牌点间隔迭代次数 为 1.5625M。 此外,假设一个农民总共有 1000 个地块。
对于 64 个标牌点中的每一个,当它们每 9.375 秒或每 1.5625M 次迭代发布到网络时,农民计算地块过滤器并查看通过的地块数量。对于每个经过的地块,农民计算所需迭代次数。
假设农民在子时隙中计算所需迭代次数 < 1.5625M 一次。(在这种情况下,我们将假设精确的所需迭代次数 = 0.7828M。)图 5 显示了在第 20 个标牌点发生的情况。
融合迭代次数然后计算为:
infusion iterations = signage point iterations + 3 * sp interval iterations + required iterations
= (signage_point * sp_interval_iterations) + (3 * sp_interval_iterations) + required_iterations
= 20*1.5625M + 3 * 1.5626M + 0.7827M
= 36.7223M
在意识到他们赢了之后(在第 20 个融入点),农民获取整个空间证明,制作一个区块(可选地包括交易),并将其广播到网络。 该块直到融合迭代次数(通常是几秒钟)才能到达时间领主,他们将融入该块,创建融入点 VDF。有了这些 VDF,区块就可以由全节点完成并添加到区块链中。
原文参考
Therefore, infusion_iterations will be between 3 and 4 signage points after the current signage point. Farmers must submit their proofs and blocks before the infusion point is reached. The modulus is there to allow overflows into the next sub-slot, if the signage point is near the end of the sub-slot. This is expanded on in Section 3.9.
More information on infusion points is available in Section 3.3.

Figure 5 shows the infusion point as a green square marked b1. The first and last blocks of the sub-slot are marked r1 and r2, respectively. For this example, the farmer will create the block at the time of the signage point marked with a red arrow, which we'll call b1'.
At b1, the farmer's block gets combined with the VDF output for that point. This creates a new input for the VDF from that point on, i.e. we infuse the farmer’s block into the VDF. b1 is only fully valid after two events have occurred:
- infusion_iterations has been reached, and
- Two VDF proofs have been included: one from
r1to the signage point and one fromr1tob1. (Actually it’s more since there are three VDF chains, explained in Section 3.8).
In Figure 5, the farmer creates the block at the time of the signage point, b1’. However, b1’ is not finished yet, since it needs the infusion point VDF. Once the infusion_iterations VDF has been released, it is added to b1’ to form the finished block at b1.
Recall that in this example,
- sub-slot_iterations = 100M
- sp_interval_iterations is 1.5625M. Furthermore, let’s say a farmer has a total of 1000 plots.
For each of the 64 signage points, as they are released to the network every 9.375 seconds, or every 1.5625M iterations, the farmer computes the plot filter and sees how many plots pass. For each passing plot, the farmer calculates required_iterations.
Let's say the farmer calculates required_iterations < 1.5625M once in the sub-slot. (We'll assume the exact required_iterations = 0.7828M in this instance.) Figure 5 shows this happening at the 20th signage point.
infusion_iterations is then computed as:
infusion_iterations = signage_point_iterations + (3 * sp_interval_iterations) + required_iterations
= (signage_point sp_interval_iterations) + (3 sp_interval_iterations) + required_iterations
= (201.5625M) + (3 1.5626M) + 0.7827M
= 36.7223M
After realizing they have won (at the 20th infusion point), the farmer fetches the whole proof of space, makes a block (optionally including transactions), and broadcasts this to the network. The block has until infusion_iterations (typically a few seconds) to reach timelords, who will infuse the block, creating the infusion point VDFs. With these VDFs, the block can be finished and added to the blockchain by full nodes.
定义#
质量字符串:空间的证据的一小部分,2 x 值出总 64 个的 x 值,可以有效地从磁盘中检索,并且该值来获取由所述标牌点来确定。
标牌点质量字符串:与挑战链标牌点连接的质量字符串的散列。这个哈希最终决定了某个证明的“运气”,以及它的所需迭代次数是低还是高。
标牌点间隔迭代:定义为 floor(子时隙迭代/64)。
标牌点:挑战和奖励链中一个子时隙内的 64 个中间时间点,VDF 会定期发布。在每个标牌点,都会创建 VDF 输出并通过网络广播。子时隙中的第一个标牌点是挑战本身。每个区块都有一个标牌点,因此区块中的空间证明必须符合该标牌点的条件。
所需迭代次数:使用质量字符串计算的数字,用于选择适合制作块的空间证明。绝大多数空间证明需要的迭代次数太高,因此不符合纳入链的条件。该数字用于计算融入点。
融入点:从挑战点开始融入迭代的时间点,用于证明具有特定挑战和融入迭代的空间。此时,农民的区块被融入奖励链 VDF。一个区块的融入点总是在该区块的标牌点之后的 3 到 4 个标牌点之间。计算为标牌点迭代 + 3 * 标牌点间隔迭代 + 所需的迭代。
标牌点和融入点之间的延迟有很多好处,包括防止孤块和自私耕作、减少分叉和没有 VDF 停顿。给出这个大约 30 秒的延迟,以便农民有足够的时间进行签名,而不会延迟时隙 VDF。行为良好的农民只在每个空间证明上签署一个标牌点,这意味着攻击者无法轻易重组链。
原文参考
Defitions#
Quality string: A small part of the proof of space, 2 x values out of the total 64 x values, which can be retrieved efficiently from disk, and which values_to_fetch is determined by the signage point.
sp_quality_string: A hash of the quality string concatenated with the challenge chain's signage point. This hash is what ultimately decides the "luck" of a certain proof, using the size of required_iterations.
sp_interval_iterations: Defined as floor(sub-slot_iterations / 64).
Signage points: 64 intermediary points in time within a sub-slot in both the challenge and reward chains, for which VDFs are periodically released. At each signage point, a VDF output is created and broadcast through the network. The first signage point in the sub-slot is the challenge itself. Each block has a signage point such that the proof of space in the block must be eligible for that signage point.
required_iterations: A number computed using the quality string, used to choose proofs of space which are eligible to make blocks. The vast majority of proofs of space will have required_iterations which are too high, and thus not eligible for inclusion into the chain. This number is used to compute the infusion point.
Infusion point: the point in time at infusion_iterations from the challenge point, for a proof of space with a certain challenge and infusion_iterations. At this point, the farmer’s block gets infused into the reward chain VDF. The infusion point of a block is always between 3 and 4 signage points after the signage point of that block. Computed as signage_point_iterations + 3 * sp_interval_iterations + required_iterations.
The delay between the signage point and infusion point has many benefits, including defense against orphaning and selfish farming, decreased forks, and no VDF pauses. This delay of around 28 seconds is given so that farmers have enough time to sign without delaying the slot VDF. Well-behaving farmers sign only one signage point with each proof of space, meaning that attackers cannot easily reorg the chain.